Microglia Dysfunction in a Mouse Model of Neurodevelopmental Disorders
Many genetic (Hayes et al. 2016) and environmental (Carloni, Ramos, and Hayes 2021) associations are risk factors for neuropsychiatric disorders. I use mouse models to investigate the basic neurobiology of some of these risk factors in disease pathophysiology. I evaluated an environmental risk factor (developmental inflammation) in disease pathophysiology using the maternal immune activation (MIA) mouse model (Hayes et al. 2021; Mueller et al. 2019). After prenatal inflammation, I found a baseline increase in stress hormones in the periphery and altered protein oxidative stress in the brain consistent with observations from clinical studies (Fukudome et al. 2018). Furthermore, I found a blunted microglia reactivity, particularly in the striatum, after MIA, along with electrophysiological abnormalities in striatal circuits (Hayes et al. 2021). The MIA microglia showed epigenetic changes and impaired transcriptional regulation in response to prenatal immune stress as a mechanism for the blunted reactivity (Hayes et al. 2021). Finally, I determined the dysfunctional microglia were causal to the proper development of the striatal circuits (Hayes et al. 2021). In summary, I determined that prenatal immune stress acts as a tolerizing stimulus on microglia leading to a long-term functional impairment and contribution to development of impaired neural circuits in the basal ganglia.
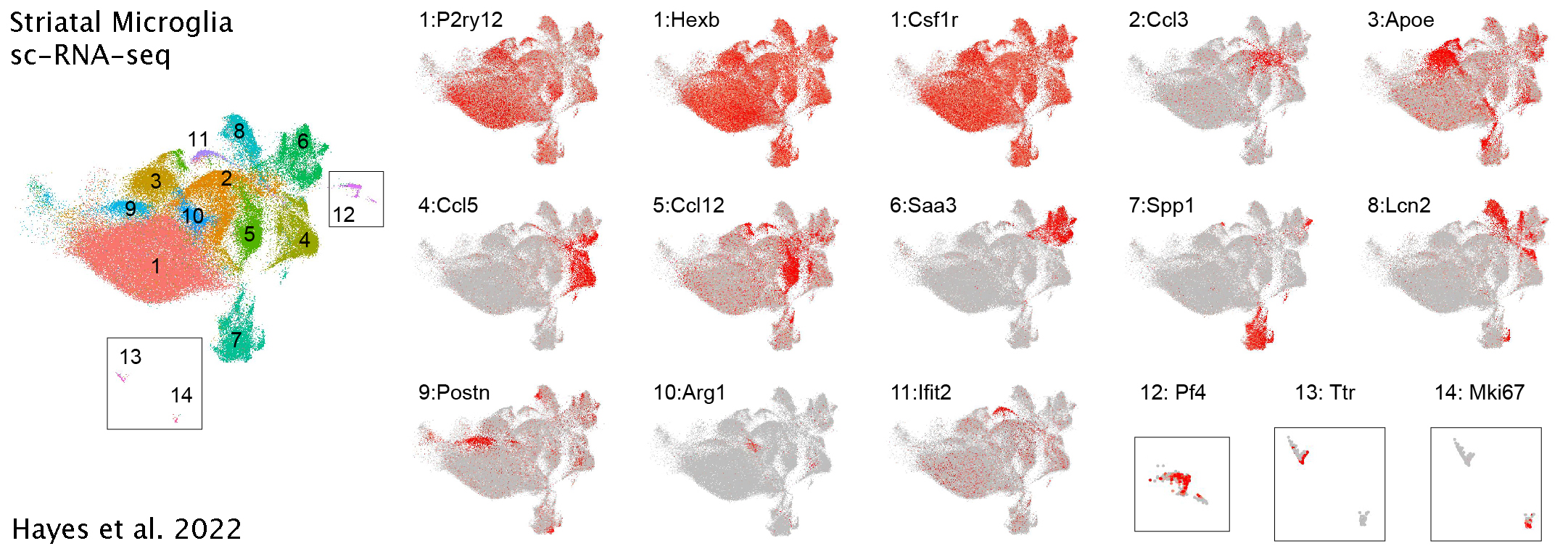
Data Analysis for Hayes et al.2022
Clinical Inflammation & Oxidative Stress
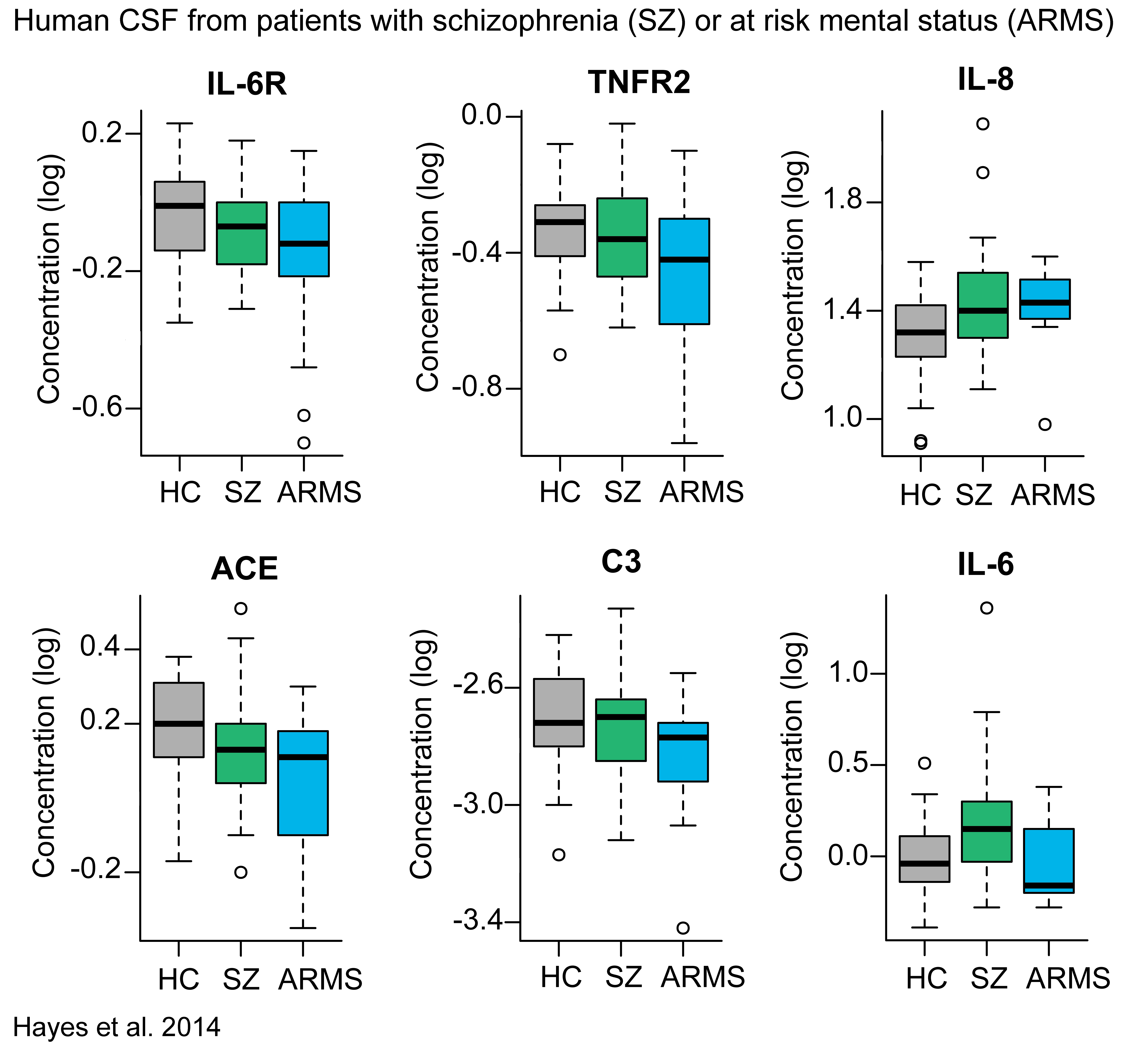
The role of inflammation and oxidative stress in psychiatric disorders remains controversial. Previous data is confounded by extended exposure to medication, duration of illness, and lack of a clear cellular mechanism. In several translational psychiatry studies, we obtained cerebrospinal fluid and peripheral blood from drug-naïve, recent-onset, and chronic psychosis patients. We found increased inflammatory markers (Hayes et al. 2014; Tanaka et al. 2017) and altered oxidative stress pathways (Coughlin et al. 2016, 2017; Nucifora et al. 2017) in schizophrenia and psychosis patients at the early stages of disease without the influence of extended medication. We observed increased levels of antibodies for infectious agents in psychosis patients, and many of the inflammatory markers were correlated with the inflammatory markers (Hayes et al. 2014). Furthermore, cognitive function was found to correlate with one of the infectious agents (Hayes et al. 2014). These data suggest that exposure to infectious agents may contribute to altered immune function in patients with psychotic disorders and impair cognitive function. Together these translational psychiatry studies provide further evidence for a neuroimmunological mechanism in the pathology of psychiatric disorders.
Developmental Biology Projects
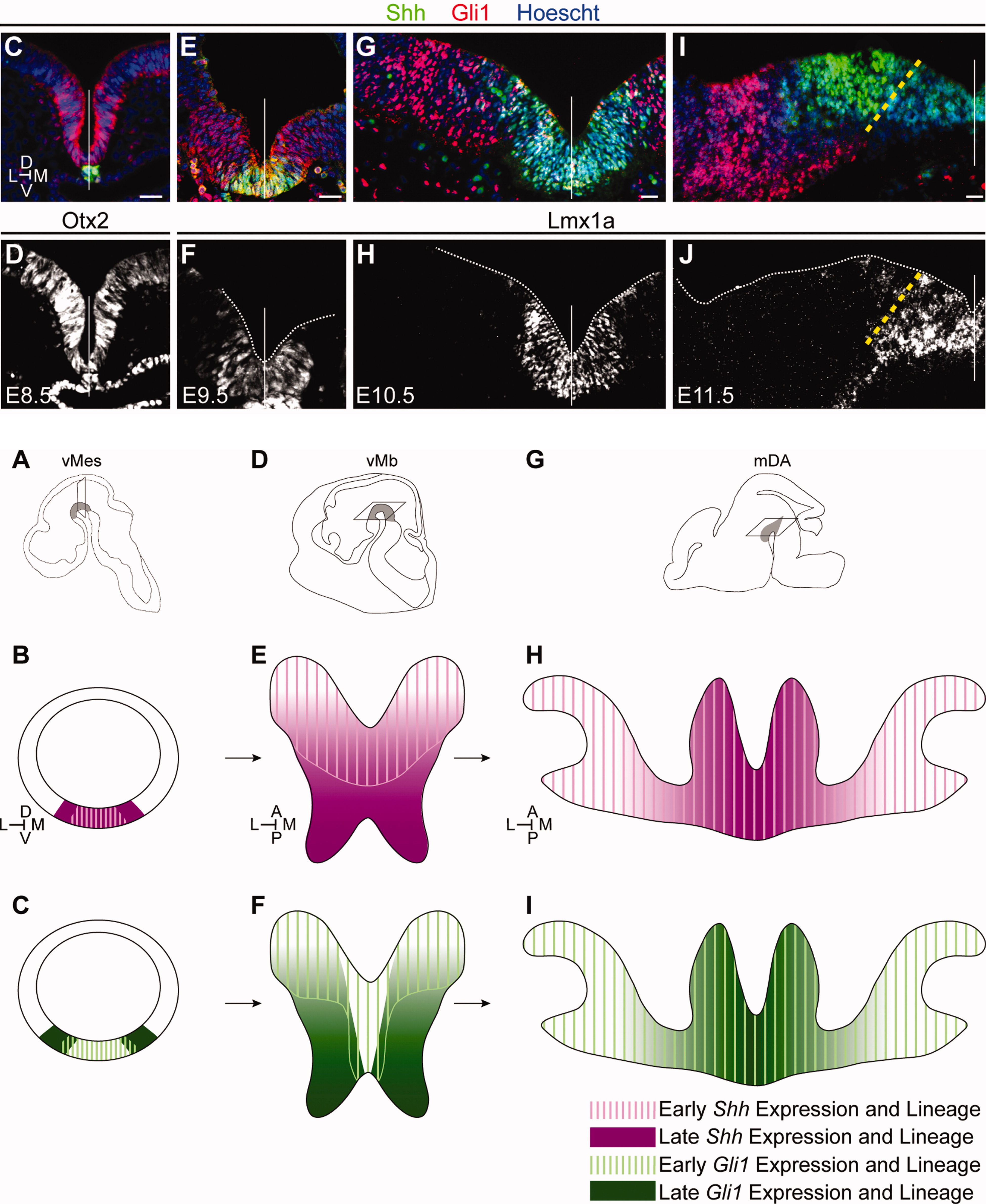
Through a number of projects we determined how diversification of cellular identity is specified from a defined progenitor domain through close temporal and spatial control of progenitor cells. Deciphering cell fate specification is important for cell-based therapeutics targeting cell replacement and discovering how cells become susceptible in disease. Using combinatorial genetic fate mapping approaches, these studies defined how progenitors become specified before differentiation based on the spatial and temporal expression of key developmental genes (Shh, Gli1, Nkx2.1, and Wnt1)(Hayes et al. 2011; Brown et al. 2011; Carney et al. 2010). Furthermore, we were the first to demonstrate that cessation of Shh signaling after the critical period is important for midbrain patterning(Hayes et al. 2013). In sum, we found that spatial location within the progenitor domain, timing of gene expression, and duration of downstream signaling are all critical for proper differentiation and subtype specification. These findings can provide a guide map for generation of specific cell types in vitro for cell replacement in neurodegenerative diseases.
Site
Created with Blogdown, Distill, and postscards